Tendinopathy Versus Tendonitis: Understanding the Differences and Implications
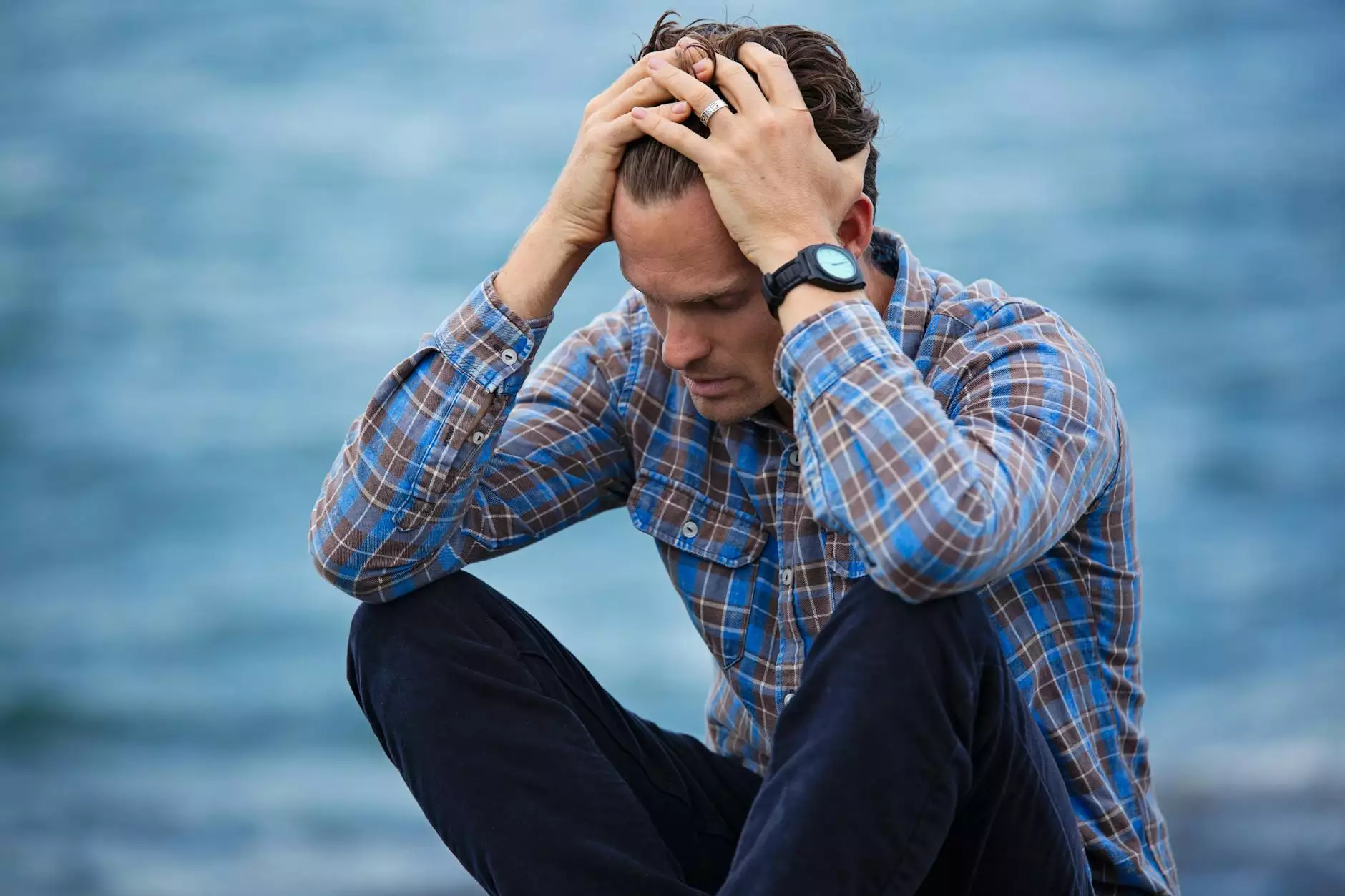

Tendinopathy and tendonitis are terms often used interchangeably, but they refer to distinct conditions that require different approaches for effective treatment and management. Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone experiencing symptoms related to tendons, whether you are an athlete, a weekend warrior, or simply experiencing discomfort in daily activities.
What Are Tendons?
Tendons are fibrous connective tissues that attach muscles to bones. They play a critical role in facilitating movement and absorbing the forces generated during physical activity. When these tendons become damaged or inflamed, issues arise that can significantly impact one's quality of life.
Differentiating Tendinopathy and Tendonitis
To fully grasp the concept of tendinopathy versus tendonitis, it’s essential to break down each term:
Understanding Tendonitis
Tendonitis is characterized primarily by inflammation of the tendon. It is often due to acute injury or repetitive strain. Common symptoms include:
- Pain and tenderness: Usually localized, particularly around the joint.
- Swelling: May be visible around the affected area.
- Stiffness: Especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
- Reduced range of motion: Difficulty moving the affected joint freely.
Understanding Tendinopathy
Tendinopathy, on the other hand, refers to a more chronic condition involving the degeneration of the tendon structure rather than inflammation. The manifestations of tendinopathy include:
- Chronic pain: Often described as a deep ache that may worsen with activity.
- Stiffness: Similar to tendonitis, but tends to persist even during rest.
- Thickening of the tendon: The tendon may feel lumpy or have a hardened area.
- Limited functionality: Activities that require strength or range of motion may become difficult.
Causes of Tendinopathy and Tendonitis
Both conditions can arise from various factors, although their underlying causes can differ:
Causes of Tendonitis
Tendonitis is often associated with acute injuries and may result from:
- Overuse: Engaging in repetitive motions without adequate rest.
- Sudden injuries: Quick movements that overload the tendon.
- Poor ergonomics: Improper techniques during physical activity or sports.
Causes of Tendinopathy
Tendinopathy typically develops over time due to chronic factors, including:
- Aging: Tendons lose elasticity and strength as we age.
- Underlying health conditions: Diabetes, obesity, and joint diseases can weaken tendons.
- Biomechanical issues: Poor posture or alignment that places excessive strain on specific tendons.
Diagnosis and Identification
Correctly diagnosing either condition is crucial for effective treatment. A healthcare professional will typically conduct:
Physical Examination
This includes assessing pain during movement, checking for swelling, and evaluating the range of motion.
Medical Imaging
X-rays, ultrasounds, or MRIs may be utilized to view the state of the tendon and rule out other injuries.
Treatment Options for Tendonitis and Tendinopathy
Effective management of tendinopathy versus tendonitis varies based on the condition's nature and severity:
Treatment Strategies for Tendonitis
- Rest: Essential to allow the inflammation to subside.
- Ice application: Helps reduce pain and swelling.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can alleviate discomfort.
- Physical therapy: Guidance on gentle stretching and strengthening exercises.
Treatment Strategies for Tendinopathy
- Gradual increase of activity: Slowly introducing movement to avoid exacerbating symptoms.
- Strength training: Focus on building tendon strength through targeted exercises.
- Therapeutic techniques: Options like ultrasound therapy or dry needling may aid in recovery.
- Cross-training: Engaging in different forms of exercise to minimize strain on the affected tendon.
The Role of Health Professionals
Health care providers such as chiropractors and physical therapists play an essential role in diagnosis and treatment. They can help facilitate recovery through:
Personalized Treatment Plans
Healthcare professionals assess individual conditions and tailor rehabilitation programs accordingly. This personal touch ensures optimal recovery and helps educate patients on their rehabilitation journey.
Education and Prevention
Understanding the risks and symptoms of both tendinopathy and tendonitis is vital for prevention. A professional can provide education on proper techniques during physical activities to reduce future risk.
Lifestyle Modifications for Prevention
Promoting tendon health goes beyond treatment; making necessary lifestyle alterations can significantly decrease the risk of both conditions. Consider the following:
Incorporating Regular Exercise
Gradual buildup of physical activity enhances tendon strength, but make sure to include:
- Stretching: Prepare your tendons for activity with appropriate stretches.
- Cross-training: Engage different muscle groups to avoid overuse injuries.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Excess body weight increases strain on tendons. A balanced diet and regular exercise are crucial to maintaining an ideal weight.
Listening to Your Body
Pay attention to pain signals. If discomfort arises, take a break and consult with a healthcare professional if necessary.
Conclusion: The Importance of Awareness and Treatment
In the debate of tendinopathy versus tendonitis, awareness and education are vital. Recognizing the differences between these conditions empowers individuals to seek appropriate treatment and implement preventive measures.
If you or someone you know is struggling with tendon-related pain, it is imperative to consult with a healthcare provider. They can help navigate the complexities of these conditions and guide you on the path to recovery. With proper care and attention, excellent outcomes are attainable, allowing individuals to return to their daily activities and regaining their quality of life.
For more information and assistance, visit iaom-us.com, where experienced professionals are equipped to help you understand and manage your tendon health effectively.